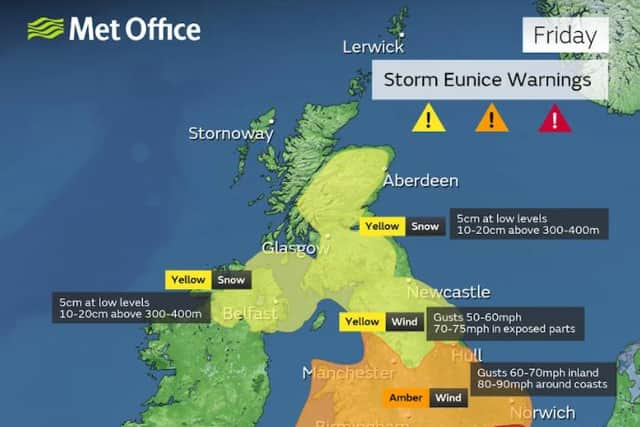
Storm Eunice: Met Office warn of weather phenomenon known as a sting jet
and live on Freeview channel 276
The forecaster defines a sting jet as a small area of very intense winds, which can be as strong as 100mph or more, that can form in powerful weather systems crossing the UK.
While the strongest winds usually take place for a short period of time, perhaps around four hours, and across an area as small as 30 miles, the Met Office said the phenomenon can cause “significant damage and risk to life”.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
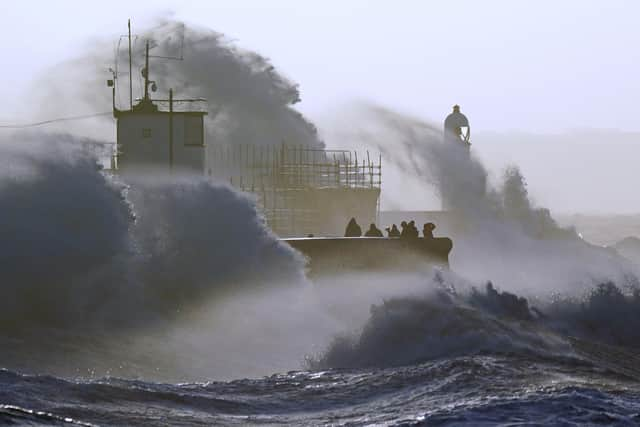
Hide AdThe so-called Great Storm in October 1987, which claimed 18 lives, is the most famous example of a sting jet forming, the forecaster said.

In that instance wind speeds reached 115mph and an estimated 15 million trees were brought down by gusts, the Met Office said.
The jets get their name from their resemblance to the sting in a scorpion’s tail, with the Met Office describing how they can be spotted as they develop on satellite images, where the end of the so-called cold conveyor is marked by a hook-shaped cloud with a point at the end.
Explaining how these jets form, the forecaster said weather fronts separate areas of warm and cold air and their interaction creates and develops wet and windy weather.


Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThere are more focused streams of warm and cold air close to the weather fronts, known as conveyor belts – with the warm conveyor rising and the cold conveyor falling.
The Met Office said these “wrap around the area of low pressure and help develop it by feeding warm air and moisture into the system”.
It added: “The cold conveyor brings its cold air from higher in the atmosphere and from being in a cold air mass. Sometimes it has help from rain and snow as they fall into it and evaporate.
“This change from liquid to gas requires heat, which is removed from the conveyor, cooling it further. Now we have even colder air falling along the conveyor, speeding up as it does so, like a rollercoaster taking the first drop.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide Ad“As this wind reaches the surface it can often produce much stronger gusts than would otherwise be made by the storm. However, the cold conveyor catches up with itself after a few hours and consumes the sting jet, keeping the length of time and area of potential damage quite small.”
During the Great Storm of 1987, the worst of the damage occurred in south-east England, with gusts of 70 knots or more recorded continually for three or four hours straight, the Met Office said.
Thousands of homes were left without power for more than 24 hours, and transport disruption was caused due to trees falling onto roads and railway lines.
The Met Office also recalled how a number of small boats were wrecked or blown away, with one ship at Dover being blown over and a Channel ferry being blown ashore near Folkestone.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe forecaster said that even the oldest at the time in the worst affected areas “couldn’t recall winds so strong, or destruction on so great a scale”.
Dr Peter Inness, meteorologist at the University of Reading, said a “strong jet stream” can “act like a production line for storms, generating a new storm every day or two”.
He added: “Eunice looks like it may be able to produce a ‘sting jet’, a narrow, focused region of extremely strong winds embedded within the larger area of strong winds and lasting just a few hours.
“Such events are quite rare but the 1987 ‘Great Storm’ almost certainly produced a sting jet, and some of the more damaging wind storms since have also shown this pattern.”
He said two red warnings for wind in a single winter is very unusual for the UK, as it is more typical to get one every two or three years.
